Constant may be defined as a quantity used in a program that cannot be
changed during program execution. There are two types of constants in C++
programming language.

const datatype identifier = value
For example, to define PI, we will use the following C++ statement
const float PI=3.1415;
1. Symbolic Constants in C++
2. Use of const qualifier
Program to input radius and calculate
circumference of circle by formula=2xpixr
By: Mahmood Alam, Instructor(IT)
Govt. Post Graduate College of Commerce,
Rahim Yar Khan
*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
float radius, circum;
const float PI=3.1415;
cout<<"Enter radius=";
cin>>radius;
circum = 2 * PI * radius;
cout<<"circumference="<<circum;
getch();
return 0;
}
#define identifier value
For example to define a symbolic constant PI with define directive, we will type:
#define PI 3.1415
1. Symbolic Constants in C++
2. Use of #define directive
Program to input radius and calculate
circumference of circle by formula=2xpixr
By: Mahmood Alam, Instructor(IT)
Govt. Post Graduate College of Commerce,
Rahim Yar Khan
*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define PI 3.1415
int main()
{
float radius, circum;
cout<<"Enter radius=";
cin>>radius;
circum = 2 * PI * radius;
cout<<"circumference="<<circum;
return 0;
}
The Difference between defining a symbolic constant by const qualifier or #define directive is:
- Literal Constants
- Symbolic Constants

1. Literal Constants
A literal constant is a value that is directly typed in a program. For example 100 or 10.50 are examples of literal constants. Literal constants can be further divided into the following categories according to the type of value:
- Integer Constant: positive or negative whole numbers like 100, 999, 2, 5056, 10, -233, -50 are called integer constants.
- Real Constants: numeric values with fractional parts like 2.45, 999.99, -5.25, -6.023 etc are called Real constants or floating point constants.
- Character Constants: a single character in single quotes like 'a', 'p' or '=' are called Character constants.
- String Constants: a set of characters in double quotations like "Enter a number" or "Asad" is called a string constant.
2. Symbolic Constants
A symbolic constant may be defined as a name given to a constant quantity in a program. A symbolic constant can be useful to make a program more readable and easier to understand. A symbolic constant is defined for a constant literal value that is frequently used in a program. For example, in a mathematical program we can use PI as symbolic constant instead of the value 3.1415.A symbolic constant can be defined in a C++ program, in two ways:How To Declare a Symbolic Constant?
1. const Qualifierconst qualifier is used to define a constant in C++ programs. The syntax is as under:
const datatype identifier = value
For example, to define PI, we will use the following C++ statement
const float PI=3.1415;
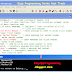
Example C Plus Plus Program Const Qualifier
/*1. Symbolic Constants in C++
2. Use of const qualifier
Program to input radius and calculate
circumference of circle by formula=2xpixr
By: Mahmood Alam, Instructor(IT)
Govt. Post Graduate College of Commerce,
Rahim Yar Khan
*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
float radius, circum;
const float PI=3.1415;
cout<<"Enter radius=";
cin>>radius;
circum = 2 * PI * radius;
cout<<"circumference="<<circum;
getch();
return 0;
}
2. define DIRECTIVEdefine preprocessor directive is also to define a constant in a C++ program. The syntax to define a symbolic constant PI with define directive is as follows:
#define identifier value
For example to define a symbolic constant PI with define directive, we will type:
#define PI 3.1415
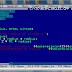
Example C Plus Plus Program #define Directive
/*1. Symbolic Constants in C++
2. Use of #define directive
Program to input radius and calculate
circumference of circle by formula=2xpixr
By: Mahmood Alam, Instructor(IT)
Govt. Post Graduate College of Commerce,
Rahim Yar Khan
*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define PI 3.1415
int main()
{
float radius, circum;
cout<<"Enter radius=";
cin>>radius;
circum = 2 * PI * radius;
cout<<"circumference="<<circum;
return 0;
}
The Difference between defining a symbolic constant by const qualifier or #define directive is:
| Sr.No. | const qualifier | #define directive |
| 1 | Here we need to define data type of constant | here we do not need to define data type of constant |
| 2 | = symbols is used | = symbol is not needed |
| 3 | This statement is terminated by semi colon. | No semi colon at end |