What is a while Loop in C++?
A while Loop in C++ and C Language is used to execute a block of one or more statements repeatedly as long as the given condition remains TRUE.When To Use a while Loop in C++?
A while Loop is suitable in a condition where the number of iteratios is not known in advance.Syntax of while Loop in C++
while(condition)
statement;
Where:
- while is the reserved word.
- condition is a valid C++ relational expression. For example i>=1 or k<=5
- statement is a C++ instruction. This instruction will be executed repeatedly as long as the given condition remains true.
or
while(condition)
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
.
.
.
statement N;
}
Where:
- while is the reserved word.
- condition is a valid C++ relational expression. For example i>=1 or k<=5
-
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
.
.
.
statement N;
}
Statement BLOCK or a compound statement A set of one or more statements enclosed in BRACES { } is called a statement block or a Compound Statement. This block will be executed repeatedly as long as the given condition remains true. This statement block is also called body of loop or Loop Body.
Working of a while loop
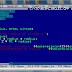
We will explain the working of a while loop in C++ with the help of an example loop statement as follows:
int counter = 1;
while ( counter <=3 )
{
cout<<"while LOOP"<<endl;
counter ++;
}
Explanation:
First of all, a loop control variable called "counter" is initialized to 1.
FIRST ITERATION
Working of while loop starts by checking the condition ( counter<=3 ). Now the value of counter is 1. So that the condition becomes 1<=3 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<"while LOOP"<<endl;
counter ++;
}
will be executed. while LOOP will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be incremented by 1 so that it has the new value 2.
SECOND ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( counter<=3 ). Now the value of counter is 2. So that the condition becomes 2<=3 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<"while LOOP"<<endl;
counter ++;
}
will be executed. while LOOP will be printed on screen for second time and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be incremented by 1 so that it has the new value 3.
THIRD ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( counter<=3 ). Now the value of counter is 3. So that the condition becomes 3<=3 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<"while LOOP"<<endl;
counter ++;
}
will be executed. while LOOP will be printed on screen for third time and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be incremented by 1 so that it has the new value 4.
Now the control will move to the start of while loop. The condition ( counter <=3 ) is tested. Since the value of counter variable is 4 now. Hence the condition becomes 4<=3 which will give false now. This will cause the while loop to end.
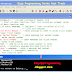
Example Code 2: Display the numbers 5 down to 1 with the help of while loop.
int k=5;
while( k >=1)
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
Explanation:
First of all, a loop control variable called "k" is initialized to 5.
FIRST ITERATION
Working of while loop starts by checking the condition ( k>=1 ). Now the value of counter is 5. So that the condition becomes 5>=1 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
will be executed. The value of k that is 5 will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable k will be decremented by 1 so that it has the new value 4.
SECOND ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( k>=1 ). Now the value of counter is 4. So that the condition becomes 4>=1 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
will be executed. The value of k that is 4 will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable k will be decremented by 1 so that it has the new value 3.
THIRD ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( k>=1 ). Now the value of counter is 3. So that the condition becomes 3>=1 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
will be executed. The value of k that is 3 will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be decremented by 1 so that it has the new value 2.
FOURTH ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( k>=1 ). Now the value of counter is 2. So that the condition becomes 2>=1 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
will be executed. The value of k that is 2 will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be decremented by 1 so that it has the new value 1.
FIFTH ITERATION
The control will move to start of while loop. Condition is checked ( k>=1 ). Now the value of counter is 3. So that the condition becomes 1>=1 which produces true result. Therefore, loop body that is
{
cout<<k<<endl;
k--;
}
will be executed. The value of k that is 1 will be printed on screen and cursor will move to next line because of endl. counter variable will be decremented by 1 so that it has the new value 0.
Now the control will move to the start of while loop. The condition ( k>=1 ) is tested. Since the value of counter variable is 4 now. Hence the condition becomes 0>=1 which will give false now. This will cause the while loop to end.














0 comments:
Post a Comment
We Love To Hear From You!